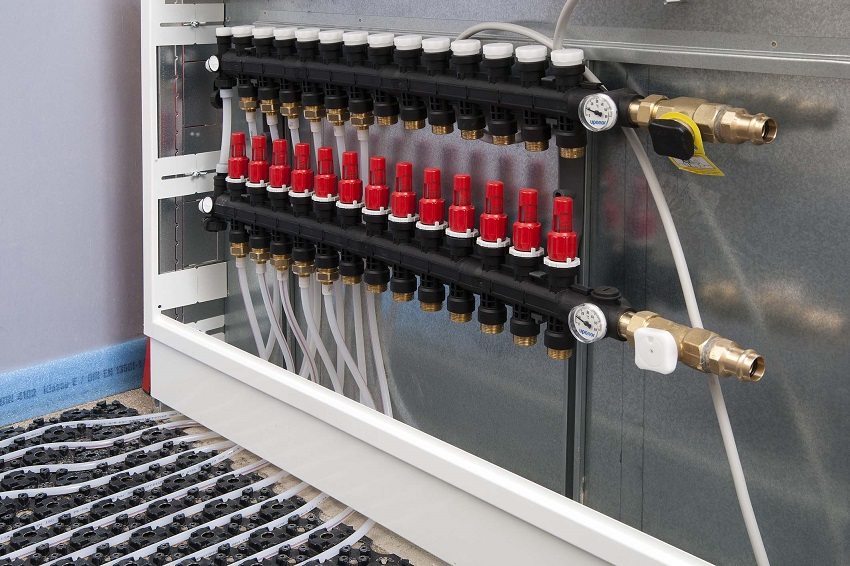
The calculation of the heat of the warm floor is carried out taking into account the heat loss through the enclosing structures and the useful area of the rooms. Calculation errors affect the operation of the system, increase energy consumption and housekeeping costs. Errors are due to the use of aggregated indicators. The efficiency of insulation and tightness of structures (foundation, load-bearing walls, ceilings, roofing, double-glazed windows, entrance doors) guarantees an economical consumption of energy resources in the system water floor heating.
A scrupulous calculation of the underfloor heating project increases the energy efficiency of the entire heating system and reduces the cost of its maintenance
Content
- 1 Appointment and calculation of heat underfloor heating
- 2 Heat carrier temperature
- 3 Underfloor heating bases
- 4 Calculations of pipes for a water-heated floor (length, diameter, pitch and methods of laying and pipes)
- 5 Floor coverings
- 6 Pumping equipment for underfloor heating calculations
- 7 Calculation of the cost of underfloor heating
Appointment and calculation of heat underfloor heating
The low-pressure heating circuit can optimize radiator heating or provide equivalent heating to the home and reduce energy costs.
The heating element and the coolant are design features that distinguish between water and electric underfloor heating. You can calculate the power of an electric underfloor heating using online calculators that are posted on specialized services on the Internet. In this article, we will take a closer look at the purpose and calculation of the power of water-heated floors.
Table 1. Recommended specific power of water floor heating per unit area:
| Design features of a residential building | Underfloor heating power, W / m2 (min / max) | |
| Additional (comfort) heating | ||
| Year of construction of the building - until 1996, climatic region - European part of Russia | 80/120 | |
| Year of construction of the building - after 1996 (improved external insulation, basement and roof insulation, double-glazed windows), climatic region - the European part of Russia | 50/80 | |
| In rooms with wooden floors (subfloor and subfloor) | 80/80 | |
| Loggias (balconies) with double glazing and insulation | 140/180 | |
| Main heating of the house | ||
| Kitchens, living rooms on the first and second floor (at least 3/4 of the heated area) | 150/∞ | |
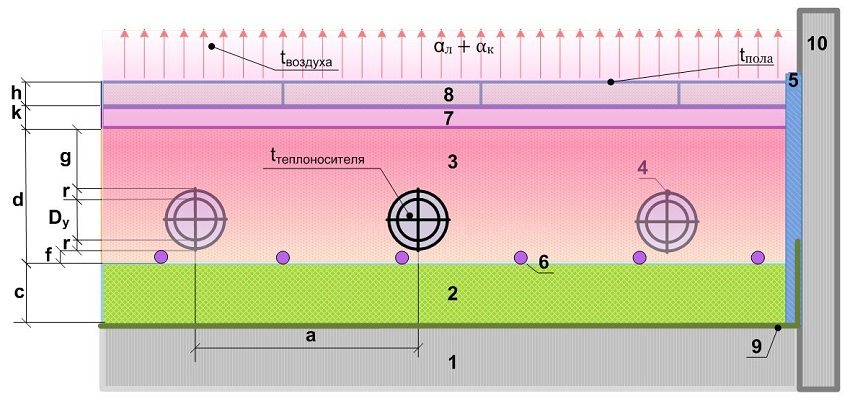
αl and αto - radiant and convective energy fluxes, W / m²;
tgender - flooring temperature, ° C;
tOK - temperature of walls and ceiling, ° C;
tair - room temperature, ° C;
S - useful area of the contour, m2.
Explanation of schemes 1 and 2 for calculating a warm floor:
|
|
Calculation of underfloor heating determines the heat consumption of a residential building in accordance with regulatory documents on thermal protection of buildings and construction heat engineering:
Q = (αl + αto) × S × (tgender - tair), (W);
tgender = Q / [(αl + αto) × S] + tair, (° C);
at S = 1m², tgender = Q / (αl + αto) + tair, (° C).
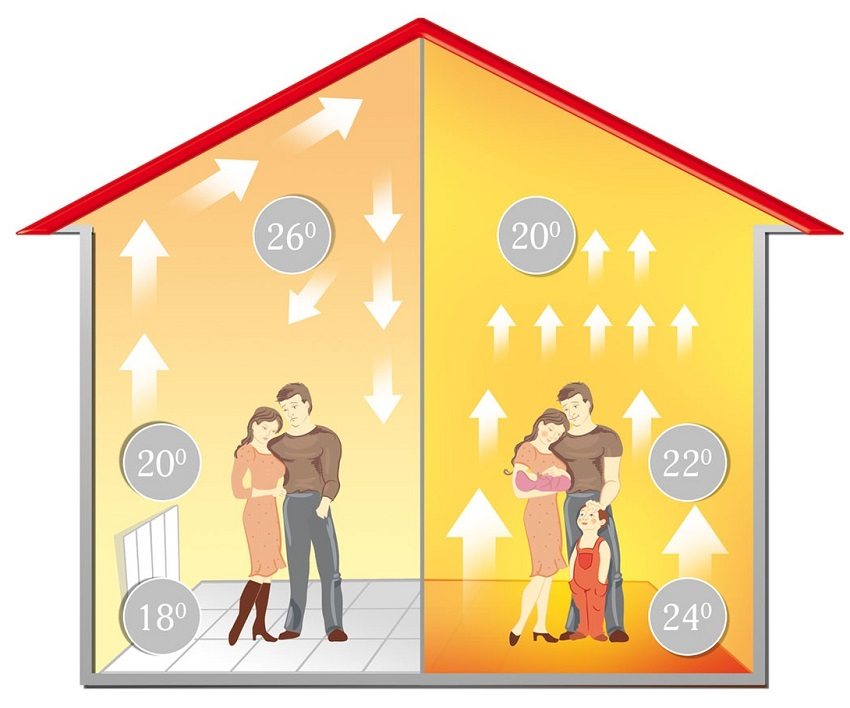
When the room temperature is heated by 1 degree, heat from the floor surface is transferred to the air:
∆t = tgender - tair = 1 ° C;
Q = (αl + αto) × S × ∆t = (4.9 + 6.1) × 1 × 1 = 11 (W).
The ideal conditions under which the heat transfer of the water circuit on one square meter of the heated floor for heating the air in the room by 1 ° C is 11 W / m². The higher the temperature in the room, the faster the room will warm up and the lower the energy consumption of the heat carrier. The underfloor heating system is preferable in order to heat insulated residential houses with permanent residence. Average admissible value of heat loss 65 W / m².
To calculate the heat transfer of a warm floor, there are special programs that can be found on the resources on the network. To clarify the issue, we suggest that you familiarize yourself with the video "Calculation of heat transfer under floor heating".
Heat carrier temperature
The temperature of the heating medium in the circuit depends on the heat load, the laying pitch, the pipe diameter, the thickness of the screed and the material of the floor covering. The minimum temperature values in the circuit are taken for parquet boards and small-piece wood products. Tiled, metlakhskaya, ceramic tiles, porcelain stoneware, marble can withstand the maximum allowed temperature of the heat carrier (55 ° C). Low-pressure heating schemes that are used in practice have an operating range of 45/35 ° C.
Sanitary standards determine the comfortable (26 ° C) and permissible temperature limit for a human foot:
- 28 ° C in living rooms for permanent residence;
- 35 ° C along the perimeter of the load-bearing walls of a residential building;
- 33 ° C for kitchens, baths and sanitary rooms.

According to sanitary standards, the temperature of the coolant in the bathroom should be 33 degrees
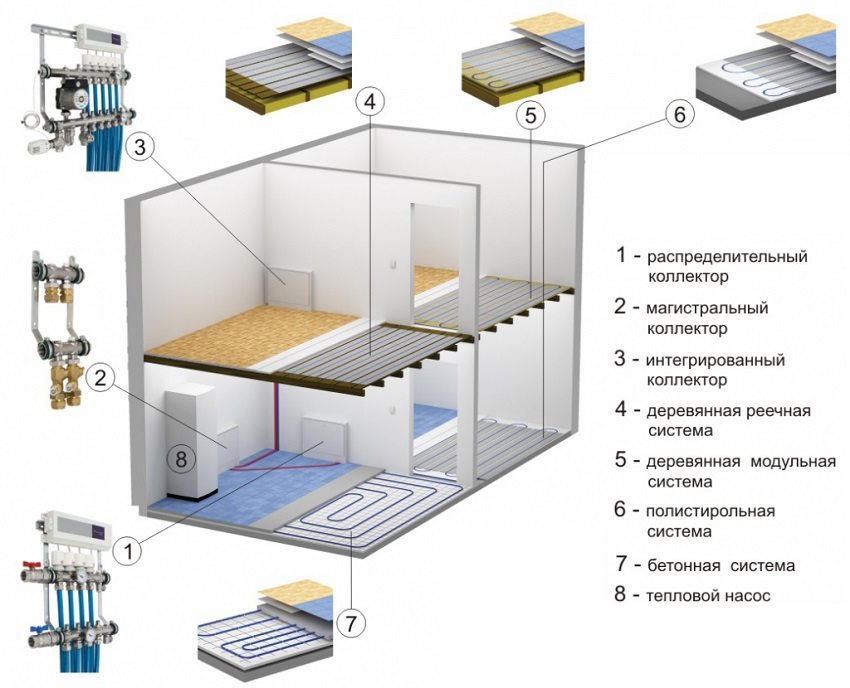
Underfloor heating bases
The type of overlap affects the materials and the choice of layer thicknesses above and below the pipe. Underfloor heating is based on cement screeds and flooring systems made of polystyrene or wooden inter-tube boards. The aluminum profile in the rack modules serves as insulating wood from direct contact with the heating element and for fastening pipes.
Related article:
Do-it-yourself water floor heating, video and description of the process. Description of the process of installing a water-heated floor. Its advantages and disadvantages, in contrast to other types of floor heating systems. Selection of materials. Video lessons.
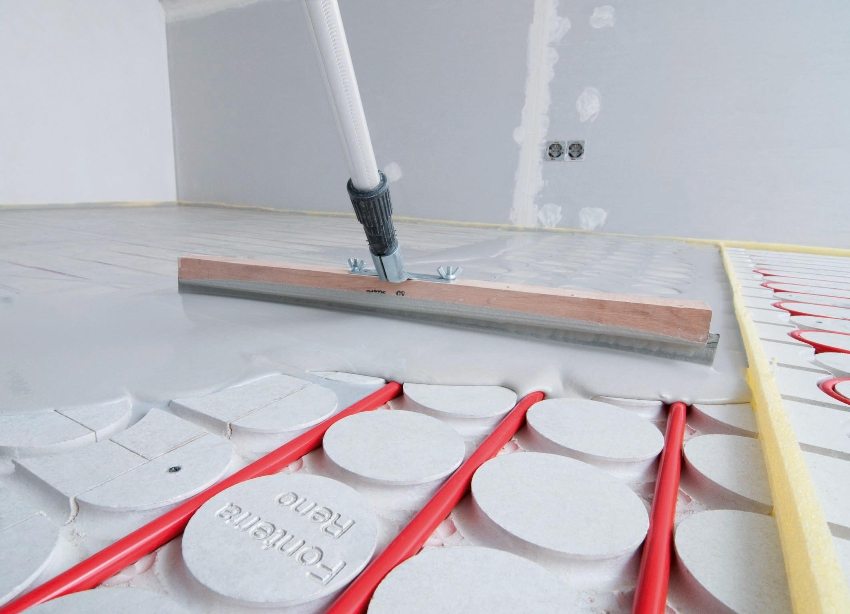
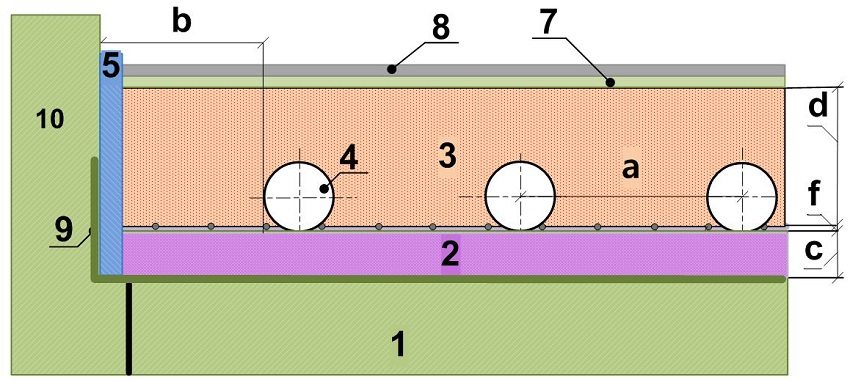
Circuit piping on concrete floor slabs arrange a concrete screed in the body. The volume of material and installation calculations of warm floors are determined after preliminary marking of the surface (hydraulic or laser level). The layout plan is carried out on paper (scale 1:50). The accuracy with which the calculation is carried out determines the consumption of material and the speed of work.
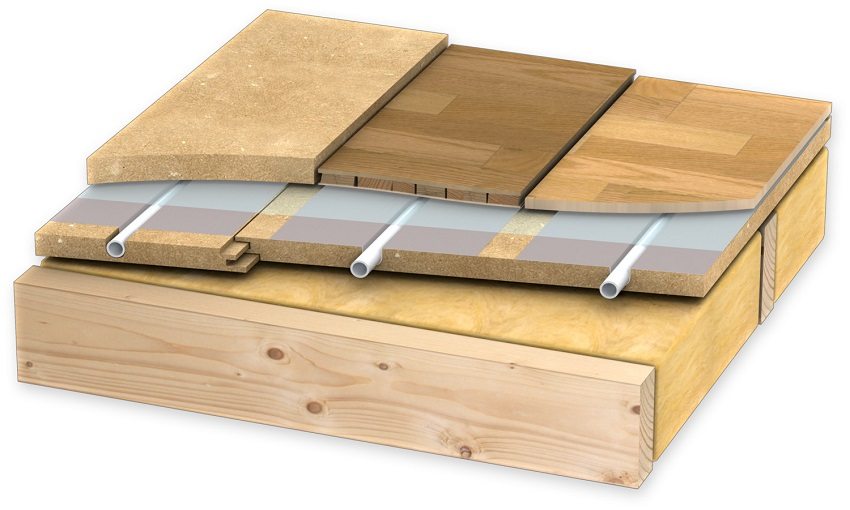

In the flat installation of the warm floor, the modular slabs have grooves for laying water floor pipes
The surface cleaned and treated with a polymer primer is leveled in advance, waterproofing is done on the soils and first floors. The walls are glued around the perimeter with a damper tape to a height that will go under the screed (with a small margin). Thermal insulation material with a foil base shields the specific heat flux upward in a given direction. Heat loss through the foil does not exceed 5%.
The reinforcement is laid on top of the insulation, the frame gives rigidity to the screed and allows you to achieve the correct fixation of the step. The pipe loop is laid out, fastened, the loop is tested under pressure and filled with a screed solution.
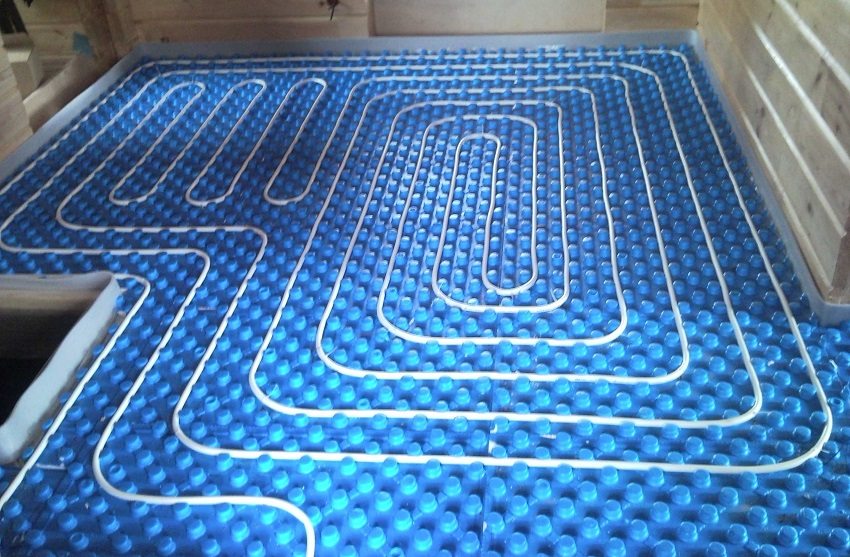
Lightweight modular systems are used for wooden structures (subfloor or logs) that do not have the ability to withstand high static loads.
Calculations of pipes for a water-heated floor (length, diameter, pitch and methods of laying and pipes)
The limited length of the low-pressure heating circuit is related to the “closed loop” effect, in which the pressure loss exceeds 20 kPa (0.2 bar). An increase in pump power, in this case not an output - the resistance will increase in proportion to the increase in pressure.

It is better to equip warm water floors in premises where they live permanently, and not use from time to time
The estimated length of pipes for a warm floor is determined by the formula:
L = (S / a × 1.1) + 2c, (m), where
L - contour length, m;
S - area, contour, m²;
a - laying step, m;
1.1 - increasing the size of the bending step (margin);
2c - the length of the supply pipes from the collector to the circuit, m.
Important! The usable room area takes into account the contour area with the addition of half the pipe pitch.
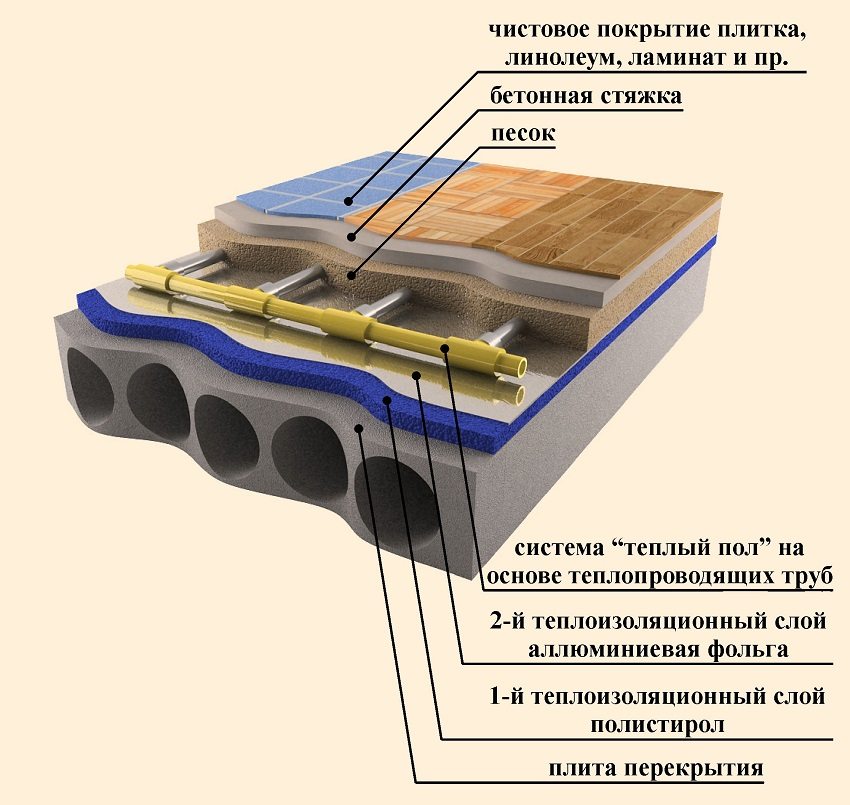
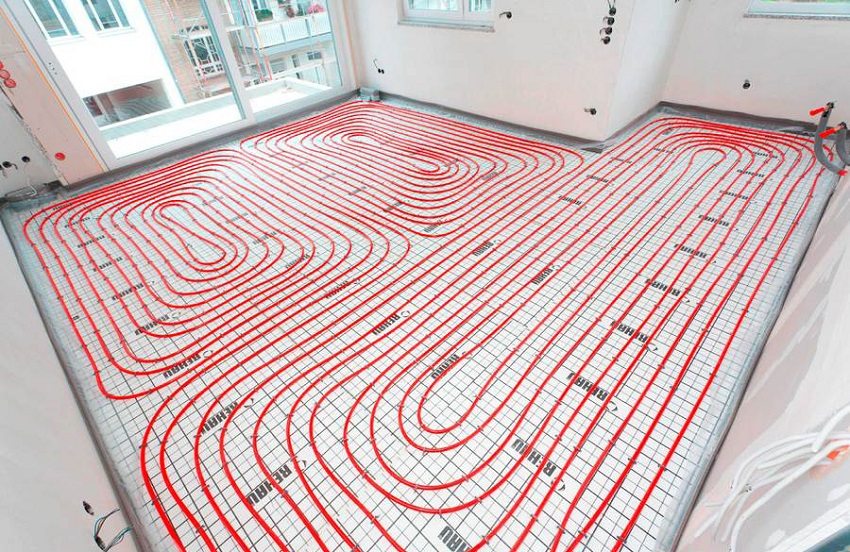
Arrangement of a warm water floor in concrete screed
The heating circuit is laid at a distance of 0.3 m from the walls. Take into account the open floor area, which transmits a uniform radiation flux. Experts do not recommend installing the heating circuit in the places where furniture is placed. Prolonged static loading can deform pipes.
With a large area of the room, the heating circuit is divided into sectors. The basic zoning rules are the aspect ratio 1/2, heating the area of one sector no more than 30 m² and keeping the same length and diameter for the chains of one collector.
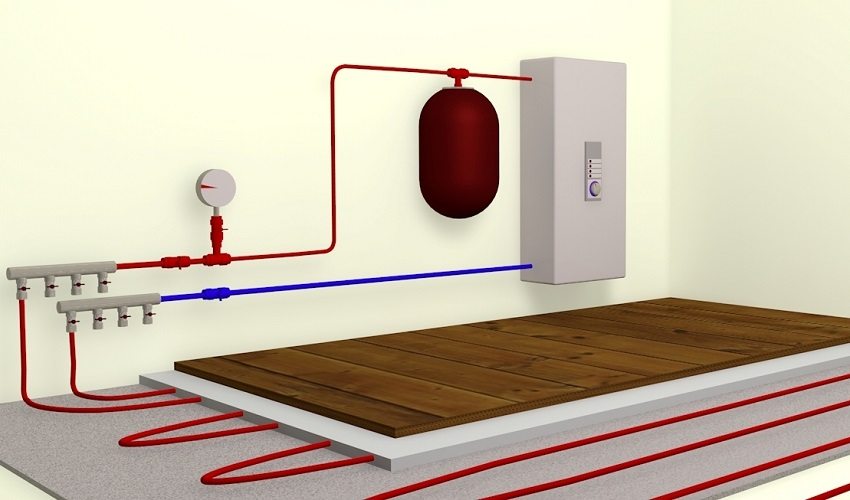
The temperature of the heating medium in the underfloor heating circuit depends on the heat load, the laying pitch, the diameter of the pipes, the thickness of the screed and the material of the floor covering
Table 2. The ratio of the lengths and diameters of the circuit pipes:
| Diameter, mm | Pipe material | Recommended loop length, m |
| 16 | metal-plastic | 80 ÷ 100 |
| 18 | cross-linked polyethylene | 80 ÷ 120 |
| 20 | metal-plastic | 120 ÷ 150 |
The diameter and pitch of the pipe layout depends on the heat load, purpose, size and geometry of the room. The heat distribution zone is proportional to the radius of the pipe. The pipe heats a section of the floor on each side of the center of the pipe. Balanced pipe spacing: Dy 16 mm - 0.16 m; 20 mm - 0.2 m; 26 mm - 0.26 m; 32 mm - 0.32 m.
The passport data of the products indicate the maximum throughput of the pipes, on the basis of which the linear pressure change is calculated. The optimal value of the speed of the coolant in the pipes water heating 0.15 ÷ 1 m / s.
Table 3. Dependence of the step on the area and sector load:
| Diameter, mm | Distance along the axes (pipe spacing), m | Optimal load, W / m2 | Total (or divided into sections) usable area of the premises, m2 |
| 16 | 0,15 | 80 ÷ 180 | 12 |
| 20 | 0,20 | 50 ÷ 80 | 16 |
| 26 | 0,25 | 20 | |
| 32 | 0,30 | less than 50 | 24 |
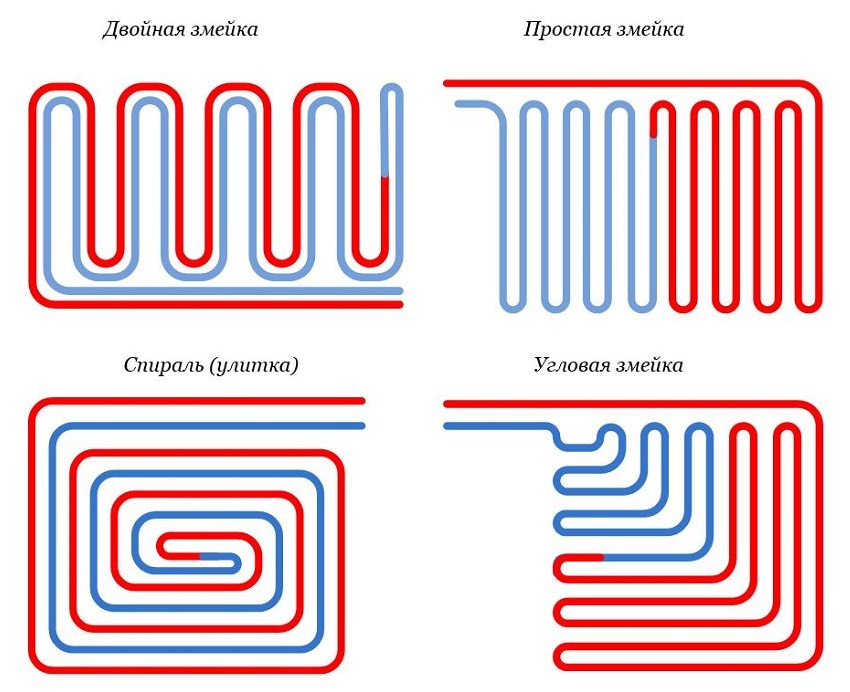
Pipe-laying options: simple, corner or double loops (snakes), spirals (snails). For narrow corridors and rooms of irregular shape, snake laying is used. Large areas are divided into sectors. Combined laying is allowed: in the edge zone, the pipe is laid out with a snake, in the main part - with a snail.
Around the perimeter, closer to the outer wall and near the window openings, the contour feed passes. The laying spacing in the edge zones may be less than the distance between pipes in the central part of the room. Connecting the reinforcements of the edge zone is necessary to increase the power of the heat flow.
Important! A 90 ° bend of pipes in a spiral scheme for connecting a water-heated floor reduces hydraulic resistance less, in comparison with laying in loops (snake).
In the calculations of pipes for a water-heated floor, diameters of 16, 20, 26, 32 mm are used.
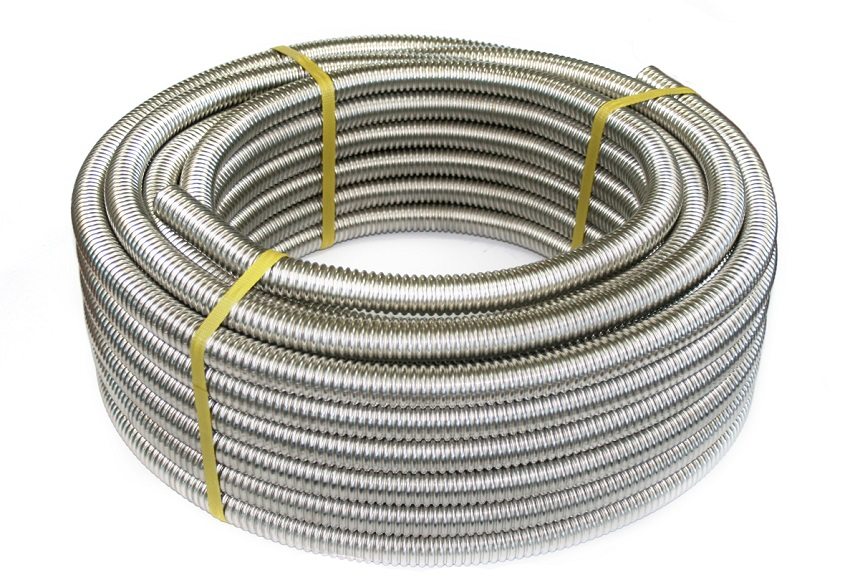
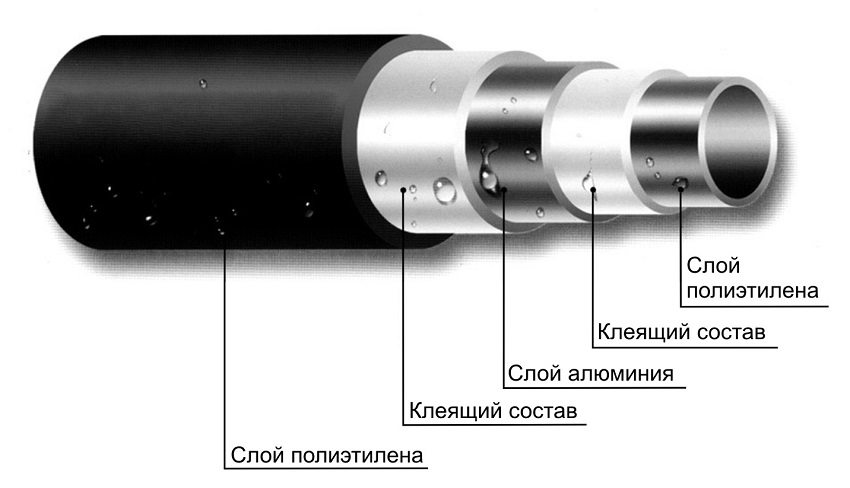
For systems of warm water floors, corrugated, stainless steel, copper, metal-plastic, cross-linked polyethylene pipelines are used. Corrugation of the pipe for underfloor heating has become relatively recent in order to facilitate the installation of the structure and reduce the cost of turning increases in length.
Polypropylene piping has a large bending radius, so it is rarely used in underfloor heating systems.
Floor coverings
Types of finishing flooring for warm floors: filling surface, linoleum, laminate or parquet, tiles, ceramic and metlakh tiles, marble, granite, basalt and porcelain stoneware.
The constant humidity in the room is contraindicated for wooden flooring, therefore it is not used in bathrooms with warm floors.
Table 4. Thermal conductivity of floor coverings:
| Material type | Layer thickness δ, m | Density γ, kg / m³ | Thermal conductivity coefficient λ, W / (m ° ∁) |
| Insulated linoleum | 0,007 | 1600 | 0,29 |
| Tiles are tiled, metlakh, ceramic | 0,015 | 1800 ÷ 2400 | 1,05 |
| Laminate | 0,008 | 850 | 0,1 |
| Parquet board | 0,015 ÷ 0,025 | 680 | 0,15 |
| Insulation (ursa) | 0,18 | 200 | 0,041 |
| Cement-sand screed | 0,02 | 1800 | 0,76 |
| Reinforced concrete slab | 0,2 | 2500 | 1,92 |
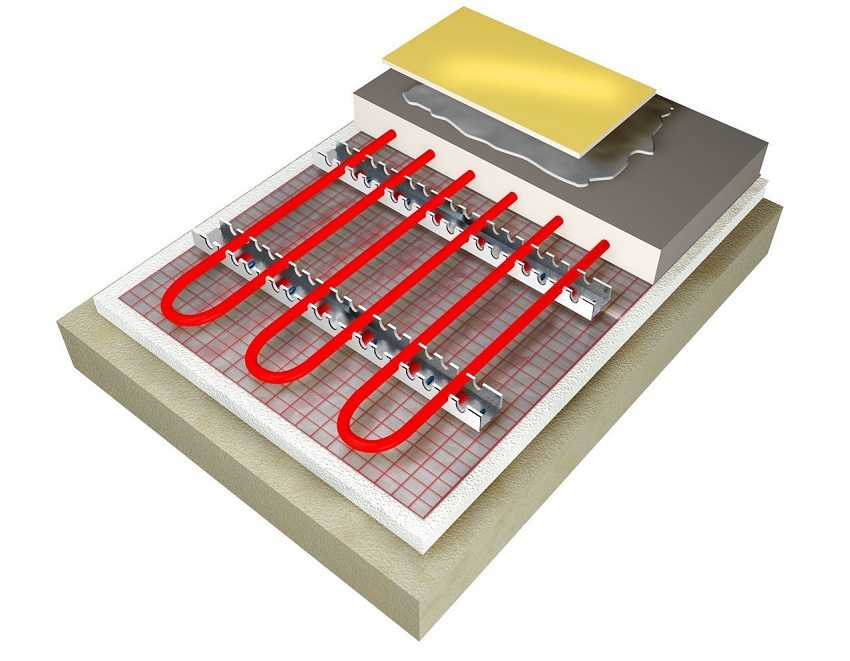
Water device warm floor in a concrete screed with a final coating of tiles
Pumping equipment for underfloor heating calculations
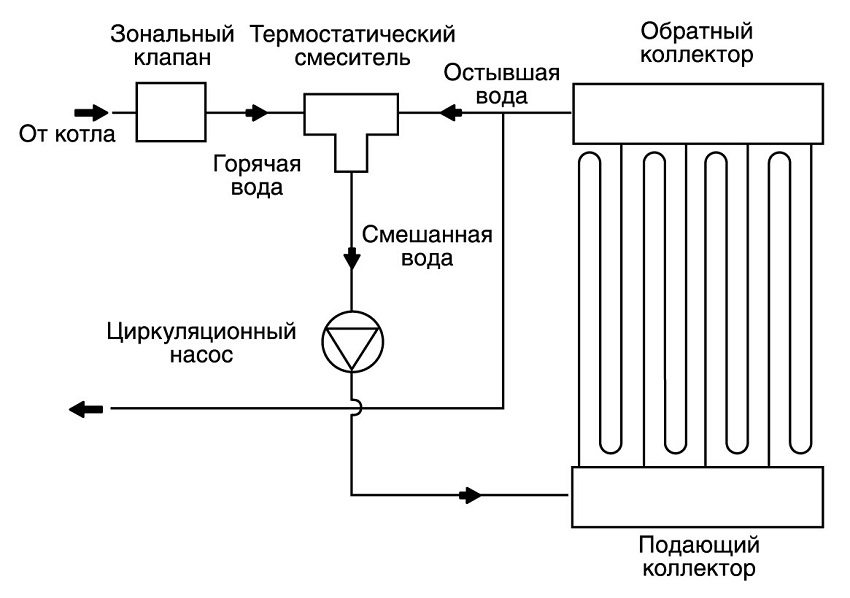
Reducing the temperature of the coolant allows you to achieve efficient operation of the circulation pumps.
The underfloor heating circuit is horizontal and covers a large area. The force that the circulating pump imparts to the flow is spent on overcoming linear and local resistances. The calculation of the pump for underfloor heating depends on the diameter, roughness of the pipe, fittings and the length of the circuit.
The main calculation parameter is the pump performance in the low-pressure circuit:
H = (P × L + ΣK) / 1000, (m), where
H is the head of the circulation pump, m;
P - hydraulic loss per running meter of length (passport data from the manufacturer), pascal / meter;
L is the maximum length of pipes in the circuit, m;
K is the power factor for local resistances.
K = K1 + K2 + K3where
K1 - resistance on adapters and tees, connections (1,2);
K2 is the resistance on the valves (1,2);
K3 - resistance at the mixing unit in the heating system (1.3).
The degree of performance possessed by the circulation pump is determined by the formula:
G = Q / (1.16 × ∆t), (m³ / hour), where
Q is the heat load of the heating circuit (W);
1.16 - specific heat capacity of water (Wh / kgC);
∆t - heat removal in the system (for low-pressure circuits 5 ÷ 10 ° С).
Table 5. Dependence of the power of the unit on the area of the heated premises (for hydraulic calculation of the warm floor):
| Floor area, m2 | Capacity of the circulation pump for underfloor heating, m³ / h | |
| 80 ÷ 120 | 1,5 | |
| 120 ÷ 160 | 2,0 | |
| 160 ÷ 200 | 2,5 | |
| 200 ÷ 240 | 3,0 | |
| 240 ÷ 280 | 4,0 | |
Helpful advice! The power of the unit consists of the sum of the costs of all circuits. In case of abnormal cold weather, it is necessary to provide a pump capacity reserve of 15 ÷ 20%.
Calculation of the cost of underfloor heating
Gas boiler and the floor hydraulic circuit connects the manifold. A uniform flow of the heat carrier is provided by automatic regulation, using balancing and thermostatic valves. The non-return valve protects the pump-mixing unit.
Table 6. Elements of a complete set of warm floor:
| Item name | Size and unit | Unit price (RUB) |
| Waterproofing | roll (1.5 × 50 m) | from 2000 |
| Damper tape | 25 m | from 500 |
| Shielding thermal insulation (expanded polystyrene) | 1100 × 800 × 38 mm | 769 |
| Trumpet | 16 ÷ 20 mm | 50 ÷ 80 |
| Concrete screed: cement dry mixes |
50 Kg 25 Kg |
125 200 |
| Collector group assembled | 2 outputs | 4600 |
| Pump and mixing unit: thermostatic head, balancing and thermostatic valves, circulation pump | set | from 20,000 |
The total cost of underfloor heating is determined by the area of the room, the equipment, the quality of the material and the method of work. Batch formation of a warm floor provides compatibility of elements and effective heating in temperature ranges. Factory equipment reduces the cost of materials by 1.5-2 times.
The owner of the house can make a calculation of water-heated floors, install the system with his own hands, if he has a sufficient stock of knowledge in heat engineering, hydraulics, materials science and experience in performing plumbing work. The mass of positive examples from life is inspiring. However, everyone should carry "their own portfolio", their own home is not a springboard for experiments.